Writing controllers
What is a controller?
In Splash, a controller is a class that contains a number of Actions. Actions are methods that can be directly accessed from the browser. What binds a URL to an action is called a route.
Controllers can be created very easily, using Splash user interface. Check it out!
Creating a controller using Splash's wizard
For your application to print some HTML when you call a URL, you need 4 things:
- A controller class: this is the class that will contain the actions declaration
- Actions methods: these are the methods that will be called when a URL is called
- A controller instance, declared in Mouf: you must create one instance of your class in Mouf (usually, only one instance)
- Views: these are files that contain the HTML to be outputed. We keep the HTML out of the controller to make the code more readable and to separate concerns between the controller (in charge of the logic) and the view (in charge of the rendering)
The Splash create-a-controller wizard will create those 4 things for you.
Let's start. Go in the MVC > Splash > Create a new controller menu.
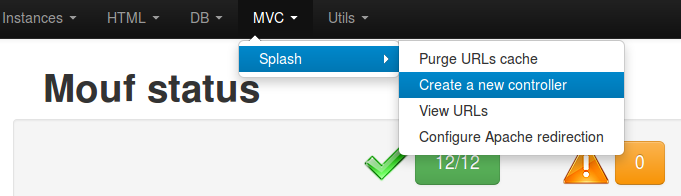
You will be displayed a page you can use to create your controller.
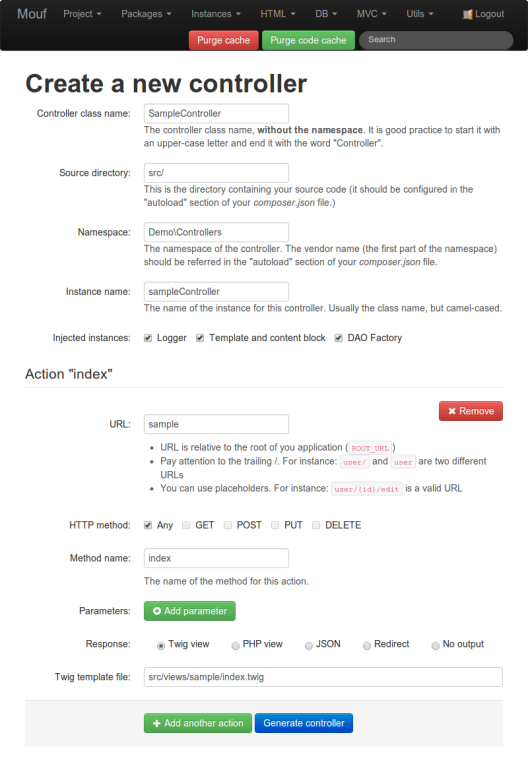
Use this page to configure your controller! You can add as many actions as you want, you can even decide what parameters must be passed to those actions. You shall also decide what instances should be injected by default in your controller (you can of course later change the class code and add more properties to the controller).
By default, you can inject in your controller:
- a logger
- an HTML template
- the content block of the HTML template
- the TDBM DAO factory (if you are using TDBM)
The @URL annotation
Have a look at the actions that have been declared:
<?php
/**
* @URL test/action
* @param int $var1
* @param int $var2
*/
public function index($var1 = 0, $var2 = 0) { ... }
?>
The @URL annotation points to the web path the action is bound to.
The action takes 2 parameters: var1 and var2. This means that the page needs both parameters passed either in GET or POST.
The @Get / @Post annotations
We might decide that an action should always be called via GET, or via POST (or PUT or DELETE if you want to provide REST services). Splash makes that very easy to handle. You can just add a @Get or @Post annotation (or @Put or @Delete). Here is a sample:
<?php
namespace Test\Controllers;
use Mouf\Mvc\Splash\Controllers\Controller;
use Zend\Diactoros\Response\HtmlResponse;
/**
* This is a sample user controller.
*
*/
class UserController extends Controller {
/**
* Viewing the user is performed by a @Get.
*
* @URL /user
* @Get
* @param string $id
*/
public function viewUser($id) {
return new HtmlResponse("Here, we might put the form for user ".htmlentities($id));
}
/**
* Modifying the user is performed by a @Post.
*
* @URL /user
* @Post
* @param string $id
* @param string $name
* @param string $email
*/
public function editUser($id, $name, $email) {
return new HtmlResponse("Here, we might put the code to change the user object.");
}
}
In the example above (a sample controller to view/modify users), the "/user" URL is bound to 2 different methods based in the HTTP method used to access this URL.
Parametrized URLs
You can put parameters in the URLs and fetch them very easily:
<?php
/**
* This is a sample user controller.
*
*/
class UserController extends Controller {
/**
* Viewing the user is performed by a @Get.
*
* @URL /user/{id}/view
* @Get
* @param string $id
*/
public function viewUser($id) {
return new HtmlResponse("Here, we might put the form for user ".htmlentities($id));
}
}
?>
Do you see the @URL annotation? The {id} part is a placeholder that will be replaced by any value found in the URL. So for instance, if you access http://[server]/[appname]/user/42/view, the $id parameter will be filled with "42".
Returning / outputting values
As you probably already guessed, you can simply "echo" things and they will show up in your browser. But you can also return a Zend-Diactoros Response object
Therefore, you can write things like:
<?php
use Zend\Diactoros\Response\HtmlResponse;
use Zend\Diactoros\Response\JsonResponse;
class MyController extends Controller {
/**
* Returning a Response object
*
* @URL /myurl1
*/
public function test1() {
return new HtmlResponse('Hello World', 200, array('content-type' => 'text/html'));
}
/**
* Returning a JSON response
*
* @URL /myjsonurl
*/
public function testJson() {
return new JsonResponse({ "status" => "ok", "message" => "Hello world!" });
}
}
?>
Typically, in Mouf, you will want to output a template object. You can easily output templates (or any object
implementing the HtmlElementInterface using the HtmlResponse object:
<?php
use Mouf\Mvc\Splash\HtmlResponse;
class MyController extends Controller {
/**
* @var HtmlElementInterface
*/
private $template;
...
/**
* Returning a Response object
*
* @URL /test_template
*/
public function test1() {
// do stuff
return new HtmlResponse($this->template);
}
}
Uploading files
Uploaded files are also directly available from the signature of the method:
HTML:
<input type="file" name="avatar" />
PHP:
<?php
use Psr\Http\Message\UploadedFileInterface;
class MyController extends Controller {
...
/**
* Uploads a file
*
* @URL /upload
*/
public function uploadLogo(UploadedFileInterface $logo) {
$logo->moveTo(__DIR__.'/uploads/logo.png');
...
}
}
The $logo object injected implements the PSR-7 UploadedFileInterface
Wanna learn more? Have a look at the advanced tutorial
Found a typo? Something is wrong in this documentation? Just fork and edit it!
