Quick start guide
In this quick start guide, we will see how you can use TDBM to query, read and write data to your database We will assume that you successfully installed TDBM using Mouf, and therefore, that TDBM is connected to your database and that the TDBM DAOs have been generated. You can learn more about DAO generation in the Generating DAOs guide.
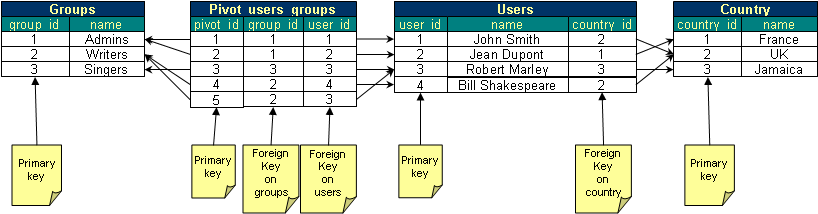
Our playground data model
For this tutorial, let's assume a very classic database schema for handling users.
- We have users. Users can be part of several groups, and obviously, a group can contain several users.
- A group has a name.
- A user has a name and is part of a country.
Connecting to the database
When you install TDBM in Mouf, you will be asked the connection to your database. This connection will be represented by a
dbalConnection instance. This instance represents a pointer to your database and can be used to execute SQL queries.
But we won't be using the dbalConnection instance. Indeed, the whole point of TDBM is to avoid writing SQL.
Upon installation, TDBM will propose you to generate the DAOs (Data Access Objects). DAOs are classes that will help you access the objects in your database. There is one DAO per table in your database. Each DAO will return "beans". Each row in your database will be represented by one instance of a bean.
Usage sample
Let's now review a few samples:
Creating a new row in the "users" table:
// Create a new bean
// Be default, you MUST pass to the bean constructor the list of all columns that are not nullable.
$userBean = new UserBean("myName");
// Fill the remaining (nullable) columns of the bean using the setters
$userBean->setPassword(password_hash("myPassword", PASSWORD_DEFAULT));
$userBean->setMail("me@mail.com");
// Any date should be passed as a PHP DateTime or DateTimeImmutable
$userBean->setCreateDate(new DateTimeImmutable());
// Finally, let's save this bean.
// For this, we need an instance of the DAO.
// The $userDao will be typically returned by the container of your application.
$userDao->save($userBean);
Since we have a "users" table, TDBM generated
a UserDao class and a UserBean class. UserDao can be used to to create/update/delete/search any
user.
You can also notice that the "save()" method is not called on the UserDao, not on the UserBean.
Retrieving a user bean by its primary key:
// Let's get the bean
$userBean = $userDao->getById(42);
// Let's display the name
echo $userBean->getName();
TDBM will automatically detect the primary key of your table (of course, your table must have a primary key). There is no name convention to respect, your primary key column can be named anything ('id', 'userid', 'isuser', ...)
To use this method, the primary key must be on a single column. If your primary key is on several columns, you can still use the search method (see below).
Querying the database
Now, what about getting the list of all users and displaying their name?
Ok, that's easy, just use the getUserList() method!
// Let's get the list of users
$userList = $userDao->findAll();
// Let's display the names
foreach ($userList as $userBean) {
/* @var $userBean UserBean */
echo $userBean->getName()."<br/>";
}
In our example, we would see
John Doe
Jean Dupont
Robert Marley
Bill Shakespeare
The findAll method will return the list of beans.
Of course, most of the time, you don't want all the rows in a database.
You want to perform a query with filters.
Querying the database on indexed columns
TDBM will do its best to help you query your database easily. In particular, if you put an index on one or many columns, it is likely that you will want to perform a query on this index. TDBM will detect the index and generate a method in the DAO.
Here is a sample:
CREATE INDEX users_status_idx ON users (status);
The users table has an index on the status column.
Automatically, TDBM will generate a findByStatus method in the UserBaseDao class:
$users = $userDao->findByStatus('on');
See how cool this is?
But wait, there is more! What about unique indexes?
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX users_login_idx ON users (login);
TDBM will generate a findOneByLogin method:
$user = $userDao->findOneByLogin('alice');
Please note how a unique index generates a findOneBy... method instead of a findBy... method.
Finally, TDBM can also deal with multi-columns indexes, or indexes on foreign keys:
CREATE INDEX users_status_country_idx ON users (status, country_id);
This index on both the status and the country_id column will be turned into a findByLoginAndCountry method:
$country = $countryDao->getById(1);
$user = $userDao->findByLoginAndCountry('on', $country);
Notice how the parameter passed for the for foreign key is a bean and not an ID.
Querying the database with filters
Now, what if I want to get something more difficult, like the list of users with name starting with a 'J'?
To do this, I need to call the find method and pass the filter in parameter.
At this point, it might be a good idea to have a look at the code TDBM did generate. For the users table, TDBM
generated 4 classes:
UserBaseDao: the base class that contains methods to access the "users" table. It is generated by TDBM. You should never modify this class.UserDao: this class extendsUserBaseDao. If you have some custom requests, you should perform them in this class. You can edit it as TDBM will never overwrite it.UserBaseBean: the bean mapping the columns of the "users" table. This class contains getters and setters for each and every column of the "users" table. It is generated by TDBM and you should never modify this class.UserBean: this class extendsUserBaseBean. If you have some custom getters and setters, you should implement them in this class. You can edit it as TDBM will never overwrite it.
In our example, we want to perform a query that retrieves any name starting with a "J". This is a new
kind of query. Since any request should be part of a DAO, we will add this request to the UserDao.
Therefore, our code will be:
class UserDao extends UserBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of users starting with $firstLetter
*
* @param string $firstLetter
* @return UserBean[]
*/
public function getUsersByLetter($firstLetter) {
// The find can be used to retrieve a list of UserBean
// It takes in parameter a SQL filter string and a list of parameters.
return $this->find("name LIKE :name", [ "name" => $firstLetter.'%' ]);
}
}
And you can simply use it like this:
$userDao = Mouf::getUserDao();
$users = $userDao->getUsersByLetter("J");
foreach ($users as $userBean)
{
/* @var $userBean UserBean */
echo $userBean->getName().'<br/>';
}
You can learn much more about filters in the advanced section of this documentation.
<
div class="alert">Very important: NEVER ever append dynamically parameters in the filter string. Use parameterized queries instead.
<
div>
You should never write something like:
// NEVER DO THIS!
$list = $this->find("name LIKE '".$firstLetter.'%"' );
Discarding parameters automatically with "Magic parameters"
TDBM helps you build queries with a variable number of parameters in a very efficient way.
Let's say you want to filter products by category and store.
Your request might look like this:
class ProductDao extends ProductBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of products filtered by category and/or store
*
* @param CategoryBean $category
* @param StoreBean $store
* @return CountryBean[]
*/
public function getProductsByCategoryAndStore(CategoryBean $category = null, StoreBean $store = null) {
return $this->find("category = :category AND store = :store", [
"category" => $category?$category->getId():null,
"store" => $store?$store->getId():null
]);
}
}
The interesting part is that TDBM will automatically discard any parameter that is set to null.
So let's imagine that your $store parameter is null. Suddenly, your filter will transform into: category = :category.
The AND store = :store will be automatically dropped by TDBM.
How is this possible? TDBM is built upon MagicQuery that has such a feature. You can read more about this feature here and here (french link).
Getting only one record
If you are confident that your query will only ever return one record (for instance, you are performing a lookup by login on the Users table, then, you can use the findOne method instead of find.
class UserDao extends UserBaseDao {
/**
* Returns a user by login
*
* @param string $login
* @return UserBean|null
*/
public function getUserByLogin($login) {
// The findOne method can be used to retrieve a single UserBean
// It takes in parameter a SQL filter string and a list of parameters.
// If will return the UserBean, or null of no user is found
// If more than 1 user is found, it will throw an exception.
return $this->findOne("login = :login", [ "login" => $login ]);
}
}
So far, so good, we have had enough play with the Users table. But the users table is not alone and it would be good to get some more information.
Navigating the object model
Many to one relationships
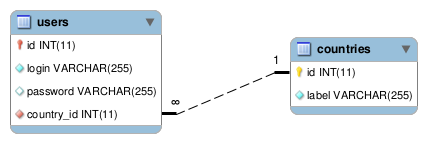
So what if I want to get the name of the country in which the first user is located?
// Let's get the user bean
$userBean = $userDao->getById(1);
// Let's get the country bean
$countryBean = $userBean->getCountry();
// Let's display the country name
echo $countryBean->getName();
Notice how you can jump from the userBean to the countryBean using the getCountry method.
The user table has a country_id column that points (through a foreign key) to the countries table, so it has a getCountry method!
Of course, there is also a setter:
$userBean->setCountry($countryBean);
Notice how you set an object rather than an ID.
One to many relationships
Ok. What, now, if I want to find a list of users from a particular country?
That's easy too.
// Let's get the country bean
$countryBean = $countryDao->getById(1);
// Let's get the users from that country
$userBeans = $countryBean->getUsers();
Many to many relationships
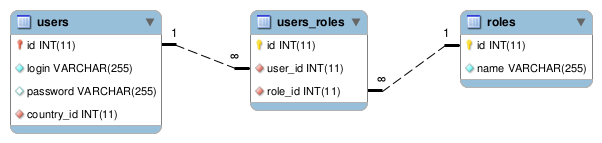
TDBM can automatically detect pivot tables in your data model. Pivot tables will have no DAO and no Beans associated. Instead, TDBM will generate a complete list of methods in the beans to edit them.
// Getter
$rolesBean = $userBean->getRoles();
// Adder
$userBean->addRole($roleBean);
// Remover
$userBean->removeRole($roleBean);
// Check existence
$hasRole = $userBean->hasRole($roleBean);
Unlike in Doctrine, TDBM does not need to have a notion of owning and inverse side of a many to many relationship.
Many to many relationships are symmetrical. Therefore, you will find the same methods in the RoleBean class:
// Getter
$usersBean = $roleBean->getUsers();
// Adder
$userBean->addUser($roleBean);
// Remover
$userBean->removeUser($roleBean);
// Check existence
$hasUser = $roleBean->hasUser($roleBean);
Joins ans filters
Simple joins
In the previous chapter, we saw how to apply filters on a table (for instance to get all users whose name starts with a 'J'). In this chapter, we will see how to apply JOINs in the filters.
In the example below, we will perform a query to get all users living in a country whose name starts by a given letter.
class UserDao extends UserBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of users whose country name starts by "$countryName"
*
* @param string $countryName
* @return UserBean[]
*/
public function getUsersByCountryName($countryName) {
// Behold the magic!
return $this->find("country.name LIKE :country", [ 'country' => $countryName.'%' ] );
}
}
Here, we called the find method passing a filter on the name column of the country table.
Behind the scene, TDBM is calling a library called MagicQuery.
MagicQuery is smart enough to automatically detect the link between the users and the countries table. You just need
to tell TDBM what filter you want on any column in any table in your database model and TDBM will find
the right query for you.
Filtering by ID/bean
Most of the time, of course, you will not pass the name of the country but the ID of the country. Actually, using TDBM you can just pass the object. Have a look!
class UserDao extends UserBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of users whose country is "$countryBean"
*
* @param CountryBean $countryBean
* @return UserBean[]
*/
public function getUsersByCountry(CountryBean $countryBean) {
// You can pass a CountryBean instance directly to the find method!
return $this->find($countryBean);
}
}
You would use this method like this:
// Let's get the country bean
$countryBean = $countryDao->getCountryById(12);
// Let's get the users from this country
$userList = $userBean->getUsersByCountry($countryBean);
// Let's display the list of users in this country
foreach ($userList as $userBean)
{
/* @var $userBean UserBean */
echo $userBean->getName().'<br/>';
}
Complex joins
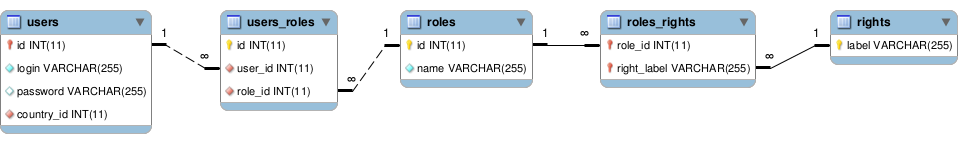
So now, what if I want to find what rights the user "Robert Marley" has?
Well this is really easy. Remember how TDBM relies on MagicQuery to find the relationship between tables? It turns out MagicQuery is clever enough to find the shortest path between any table in your data model. This means your code can look like this:
class RoleDao extends RoleBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of roles for a given user
*
* @param UserBean $user
* @return RoleBean[]
*/
public function getRolesForUser(UserBean $user) {
// Behold the magic!
return $this->find($user);
}
}
Powerful, isn't it? TDBM automatically detected the two pivot tables and performed 4 joins to retrieve the roles our user has.
Simple filter syntax
If your filter is only made of "=" and "AND" statements, you can use the shortcut "array" syntax in your queries.
Here, we filter a products table by category_id and status:
class ProductDao extends ProductBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of products filtered by category_id and status
*
* @param int $category_id
* @param int $status
* @return ProductBean[]
*/
public function getRolesForUser(int $category_id, int $status) {
return $this->find([
'category_id' => $category_id,
'status' => $status,
]);
}
}
Ordering
You can get your results in a specific order using the third parameter of the find method:
class UserDao extends UserBaseDao {
/**
* Returns the list of users by alphabetical order
*
* @return UserBean[]
*/
public function getUsersByAlphabeticalOrder() {
// The third parameter will be used in the "ORDER BY" clause of the SQL query.
return $this->find(null, [], 'name ASC');
}
}
Restricting results fetched using limits and offsets
Let's now learn how to use limit and offsets to limit the number of results fetched in a query.
Found a typo? Something is wrong in this documentation? Just fork and edit it!