Supported injection techniques
Finished the video? In a hurry? Directly jump to the next video about supported types >
When you work with Mouf, you can inject dependencies or parameters in your instances. If you want to use Mouf UI for dependency injection, you can use 3 types of injection:
Injecting values in constructor arguments
Mouf can inject values/instances in any constructor argument (actually, any argument that is not compulsory MUST be configured in Mouf, otherwise, Mouf won't be able to instantiate the object).
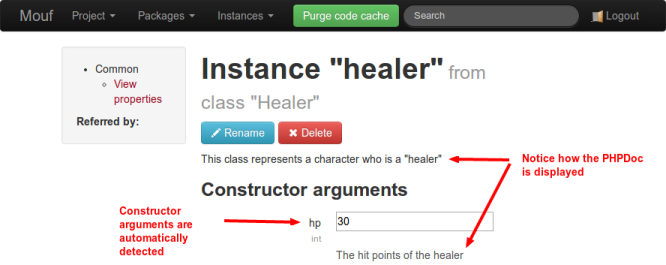
In this sample, we will be modeling a "Healer". A Healer MUST have hit points (therefore, it is an argument passed to the constructor).
Sample
/**
* This class represents a character who is a "healer"
*/
class Healer {
private $hp;
...
/**
* @param int $hp The hit points of the healer
*/
public function __construct($hp) {
$this->hp = $hp;
}
...
}

Injecting values in setters
Mouf can inject values/instances in any setter. A setter is a method whose name starts with "set" and that takes olny one argument.
Sample
class Healer {
private $potions;
...
/**
* The list of potions the Healer possesses.
*
* @param array<PotionInterface> $potions
*/
public function setPotions(array $potions) {
$this->potions = $potions;
}
...
}


Public properties injection
Mouf can inject values/instances in any public property.
Sample
class Healer {
...
/**
* The list of potions the Healer possesses.
* @var array<PotionInterface>
*/
public $potions;
...
}


Type inference
Mouf has 2 strategies to infer the type of a parameter:
It will first look if the parameter has an explicit type (for constructor arguments and setters). For instance:
public function __construct(MyClass $parameter);In this function, the "MyClass" type is declared in the function signature. It is easy.
If the type is not available, Mouf will fallback to annotations to get the type. For instance:
/** * @param MyClass $parameter */ public function __construct($parameter) { $this->parameter = $parameter; }The @param annotation will be used to define the type of the
$parametervariable. If we were playing with public fields, we would use:/** * @var MyClass */ public $parameter;
Found a typo? Something is wrong in this documentation? Just fork and edit it!